What is Angular ngSwitch Directive?
The ngSwitch directive is a structural directive, which is used to add or remove elements from the DOM. It works with ngSwitchcase and ngSwitchDefault directives.
Note:- Angular ngSwitch Directive is a similar to the switch statement of JavaScript.
It is used to bound the container element like div etc.
Example:- In the below example, we defined property permissionStatus into the ngSwitch and if, it exists then it will check otherwise not.
<div class="text-align-center" [ngSwitch]="permissionStatus">
</div>
ngSwitchcase
It is used to bound to an inner element, which is used inside the container element. It works like a switch case condition in JavaScript.
We use * (Asterix symbol) before the ngSwitchcase because it is a structural directive. We also assign a matchexpression like , which Angular evaluates at runtime. The Angular displays the inner element only when the value of the matchexpression matches the value of the switchexpression else it is removed from the DOM.
Example:- In the below example, we defined two ngSwitchCase which has value Allow and disallow.
<span *ngSwitchCase="'allow'">
It is accepted
</span>
<span *ngSwitchCase="'disallow'">
It is rejected
</span>
ngSwitchDefault
It works same as default in switch case condition in JavaScript. It does not have any match expression. It is also used into an inner element, which we must place inside the container element.
If no one ngSwitchCase matches in the switch expression, then the angular displays the element which is attached to the ngSwitchDefault.
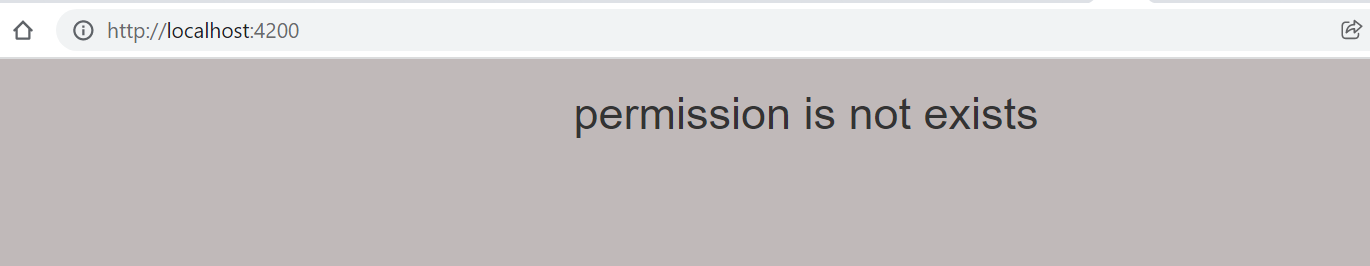
Example:- In the below example, we defined ngSwitchDefault this condition will call when none of condition match in switch statement.
<span *ngSwitchDefault>
permission is not exists
</span>
complete example of ngSwitch, ngSwitchcase and ngSwitchDefault
Step1) Now put the below code into app.component.ts file and defined the permissionStatus value is allow.
import { Component, OnInit} from '@angular/core';
@Component({
selector: 'app-root',
templateUrl: './app.component.html',
styleUrls: ['./app.component.scss']
})
export class AppComponent implements OnInit{
permissionStatus: string = 'allow';
constructor(){
}
ngOnInit() : void{
}
}
Step2) Now, put the below code into app.component.html file.
<div class="text-align-center" align="center" [ngSwitch]="permissionStatus">
<span *ngSwitchCase="'allow'" style="color:green">
<h2>It is accepted</h2>
</span>
<span *ngSwitchCase="'disallow'" style="color:red">
<h2>It is rejected</h2>
</span>
<span *ngSwitchDefault>
<h2>permission is not exists</h2>
</span>
</div>
Step3) When open the URL
http://localhost:4200/
Scamnerio-2
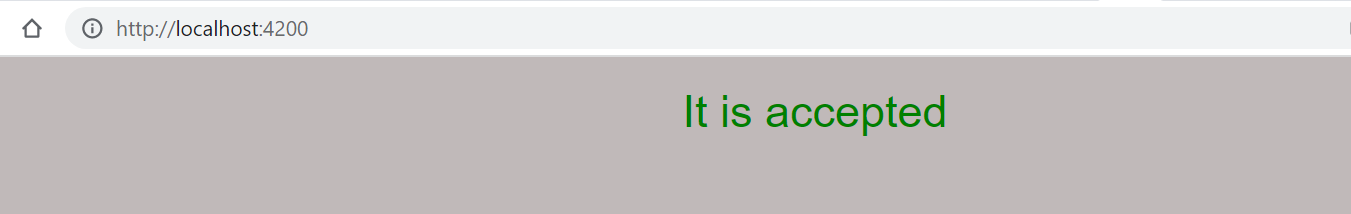
If we put the permissionStatus value disallow into the app.component.ts file.
permissionStatus: string = 'disallow';
then the output

Scamnerio-3
If we put the permissionStatus value like test into the app.component.ts file
permissionStatus: string = 'test';
then the output